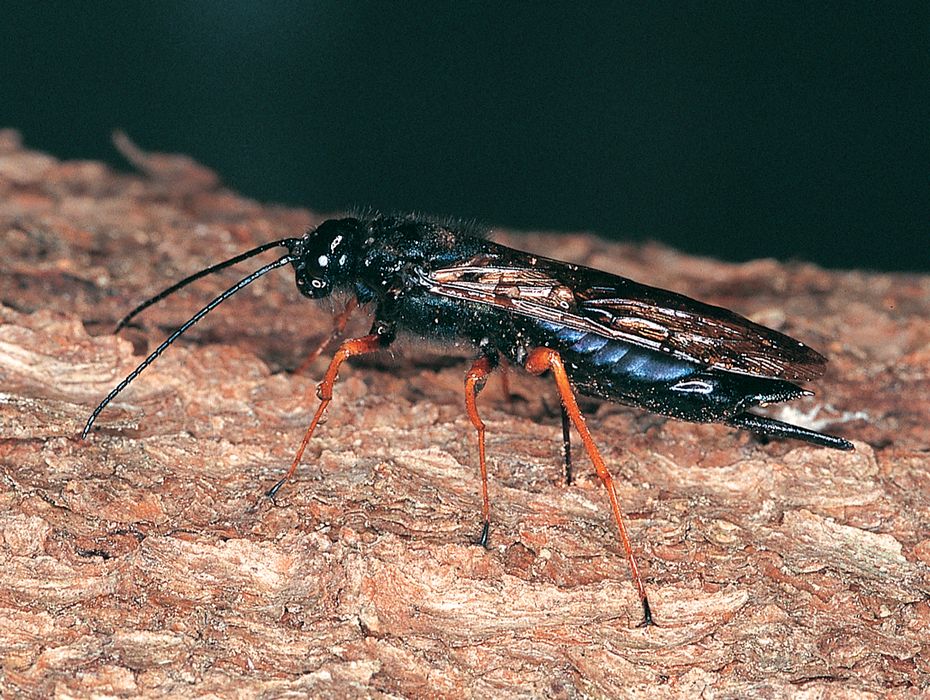
References
|
Boissin, E., B. Hurley, M. J. Wingfield, R. Vasaitis, J.
Stenlid, C. Davis, P. de Groot, R. Ahumada, A. Carnegie, A. Goldarazena,
P. Klasmer, B. Wermelinger & B. Slippers. 2012. Retracing the routes
of introduction of invasive species: the case of the Sirex noctilio
woodwasp. Molecular Ecology
5728–5744. doi:10.1111/mec.12065.
Foelker, C. J., Standley, C. R., Fierke,
M. K., Parry, D. and Whipps, C. M. 2015.
Host tissue identification for cryptic
hymenopteran parasitoids associated with
Sirex noctilio. Agricultural and
Forest Entomology. doi:
10.1111/afe.12137
Hurley B.P., Slippers, B. &
Wingfield, M.J. 2007. A comparison of control results for the alien
invasive woodwasp, Sirex noctilio, in the southern hemisphere.
Agricultural and Forest Entomology 9: 159–171.
Slippers, B., Coutinho, T.A.,
Wingfield, B.D. & Wingfield, M.J. 2003. The genus Amylostereum
and its association with woodwasps: a contempary review. South
African Journal of Science 99: 70 – 74.
Slippers, B., Wingfield, M.J.,
Coutinho, T.A. & Wingfield, B.D. 2001. Population structure and
possible origin of Amylostereum areolatum in South Africa.
Plant Pathology 50: 206 – 210.
Slippers B.,
Wingfield, B.D., Coutinho
T.A. & Wingfield M.J. 2002.
DNA sequence and RFLP data reflect geographical spread and relationships
of
Amylostereum areolatum and its insect vectors.
Molecular Ecology 11: 1845-1854.
Taylor, J.S. 1962. Sirex
noctilio F., a recent introduction in South Africa .
Entomologist’s Record 74: 273 – 274 .
Tribe, G.D . 1995. The woodwasp
Sirex noctilio Fabricius (Hymenoptera: Siricidae), a pest of
Pinus species, now established in South Africa. African Entomology
3: 215 – 217.
Tribe , G.D. & Cillié , J.J . 2004. The spread of Sirex
noctilio Fabricius (Hymenoptera: Siricidae) in South African pine
plantations and the introduction and establishment of its biological
control agents. African Entomology 12: 9 – 17.
Picker,
M., Griffiths, C & Weaving, A. 2002. Field Guide to Insects of South
Africa. Struik Publishers, Cape Town.
van
Noort, S. & Picker, M.
2011.
Wasps, Bees, Ants. Class Insecta, Order Hymenoptera.
Pp 140-146. In:
Picker,
M. & Griffiths, C. (eds.)
Alien & Invasive Animals. A South African perspective.
Struik Nature.
|