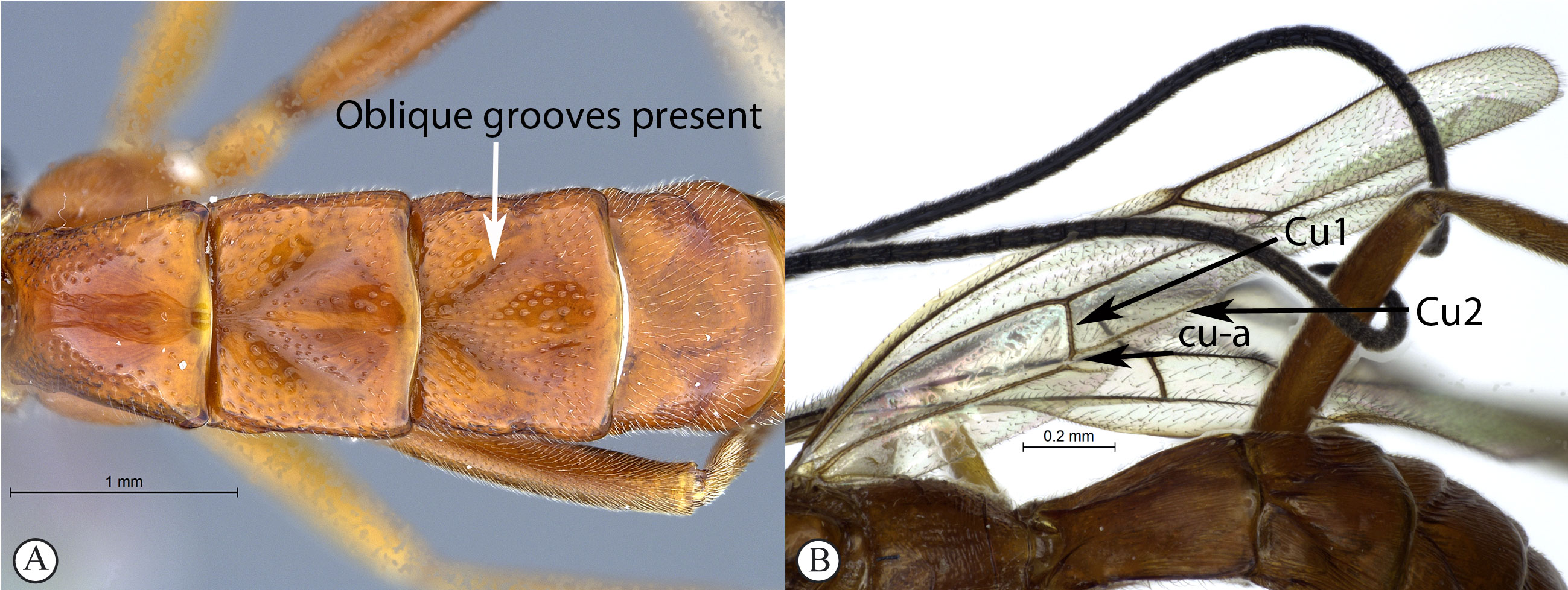

1.
Tergites 2–4 with a median pair of (usually) deep oblique grooves
that converge anteriorly and diverge posteriorly (A); Cu1 longer
than cu-a, such that Cu2 arises below middle of these combined veins
(nervellus of Townes) (B) …2

- Tergites 2–4 without a median pair of oblique grooves (a); Cu1
often longer than cu-a, but may be shorter (b) ...4
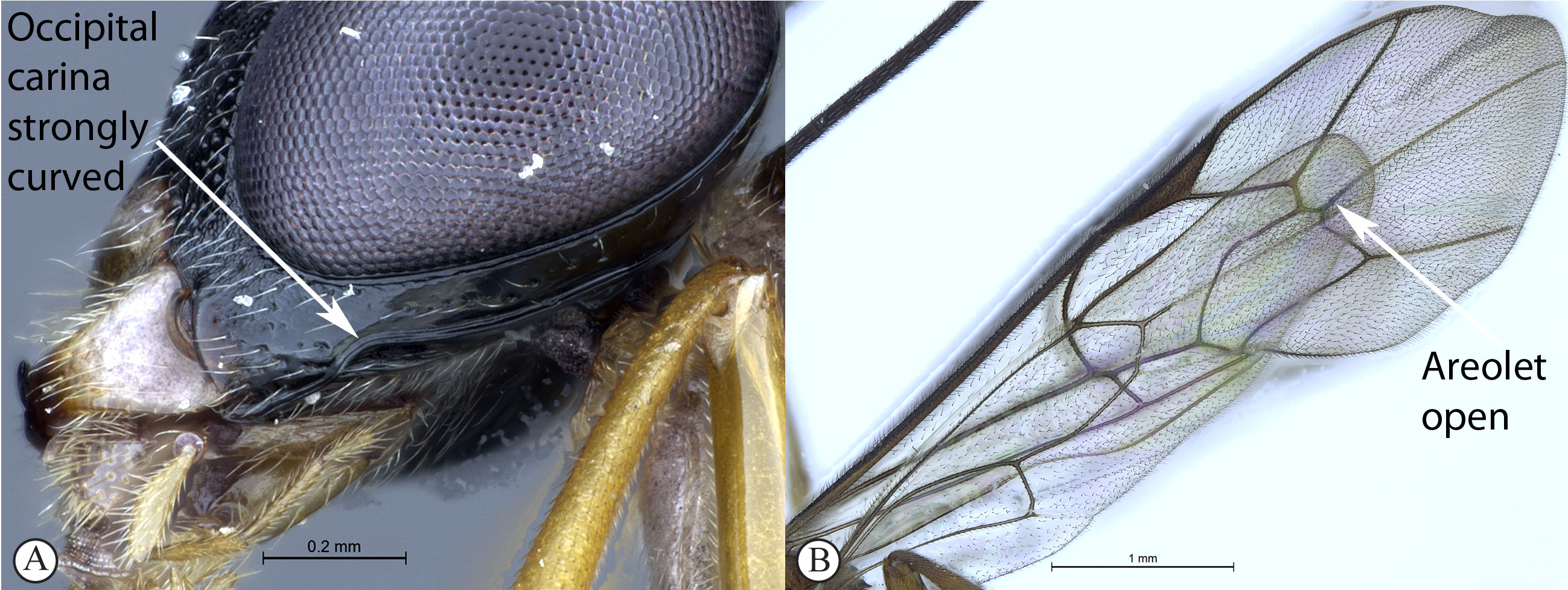

1.
Occipital carina strongly curved before junction with hypostomal
carina (A); areolet open, i.e. vein 3rs-m absent (B) ...Apophua

- Occipital carina without a strong curve before junction with
hypostomal carina (a); areolet closed (b)...3
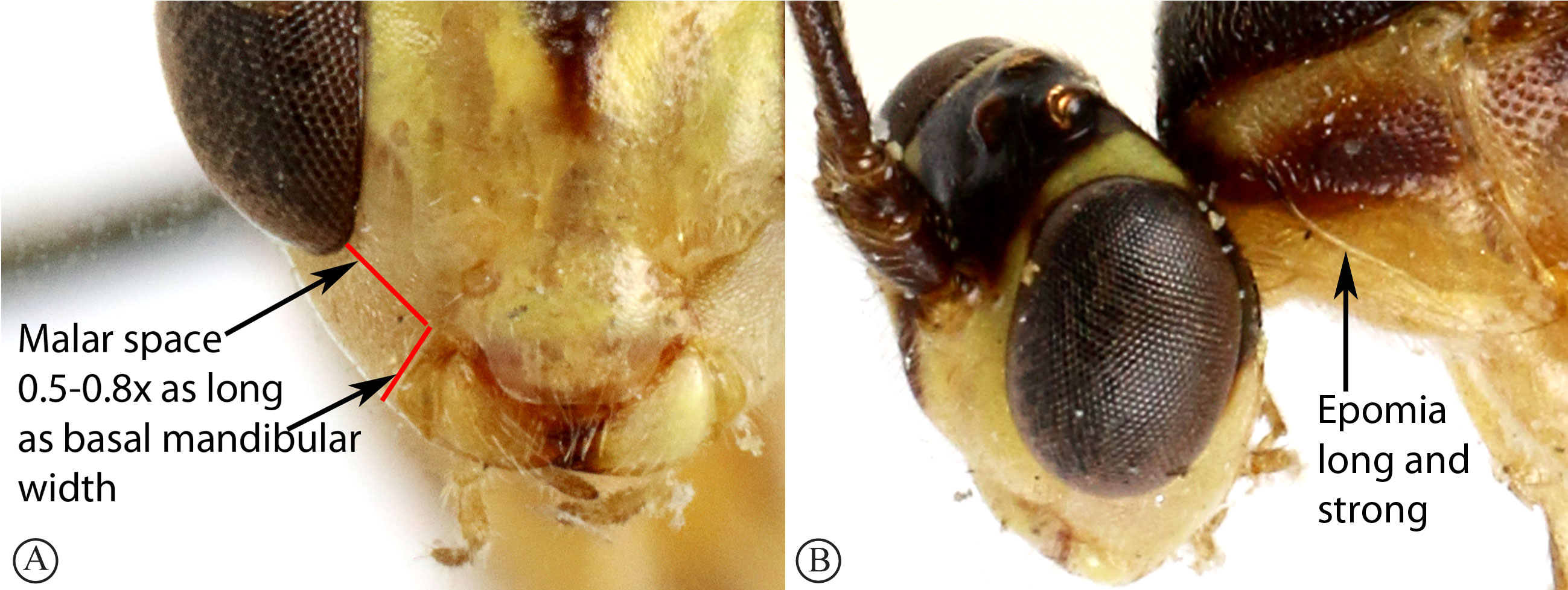

3. Malar space 0.5 to 0.8× as long as basal width of mandible (A);
epomia long and strong (B) ...Glyptopimpla
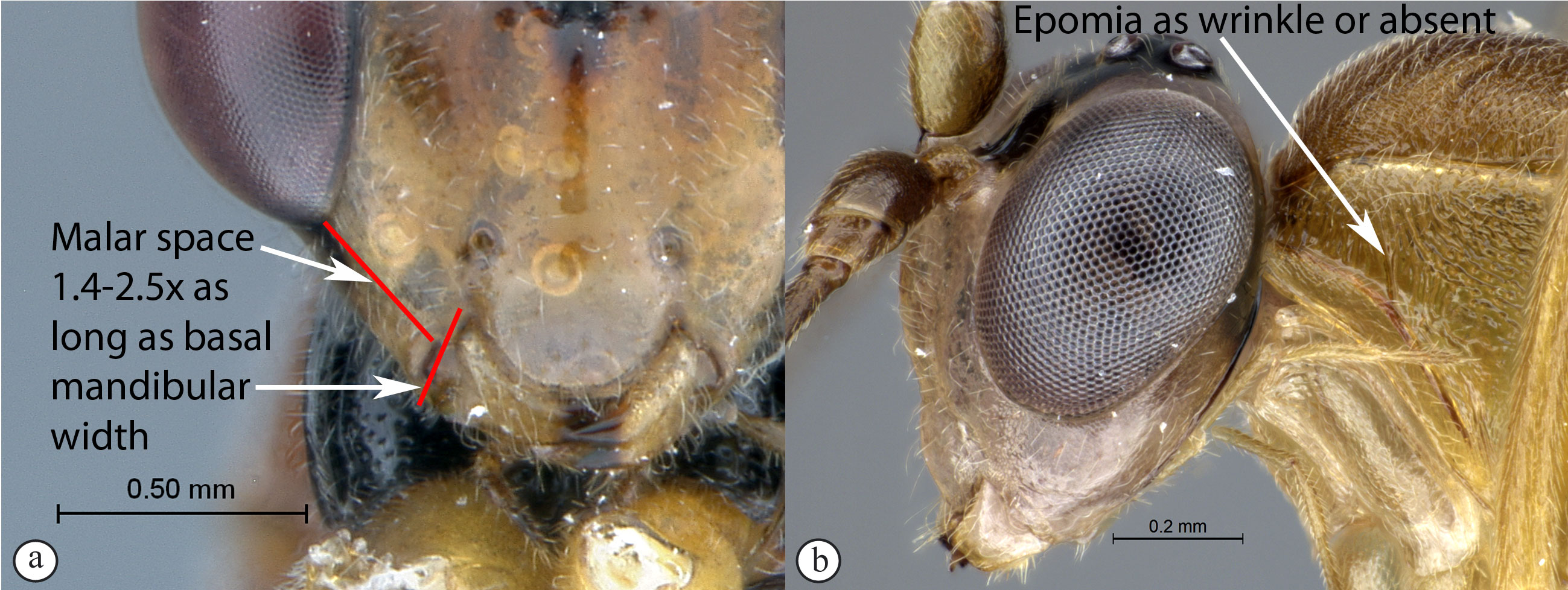

- Malar space 1.4 to 2.5× as long as basal width of mandible (a);
epomia usually absent or indistinct, only represented as a short
wrinkle (b) ...Sjostedtiella
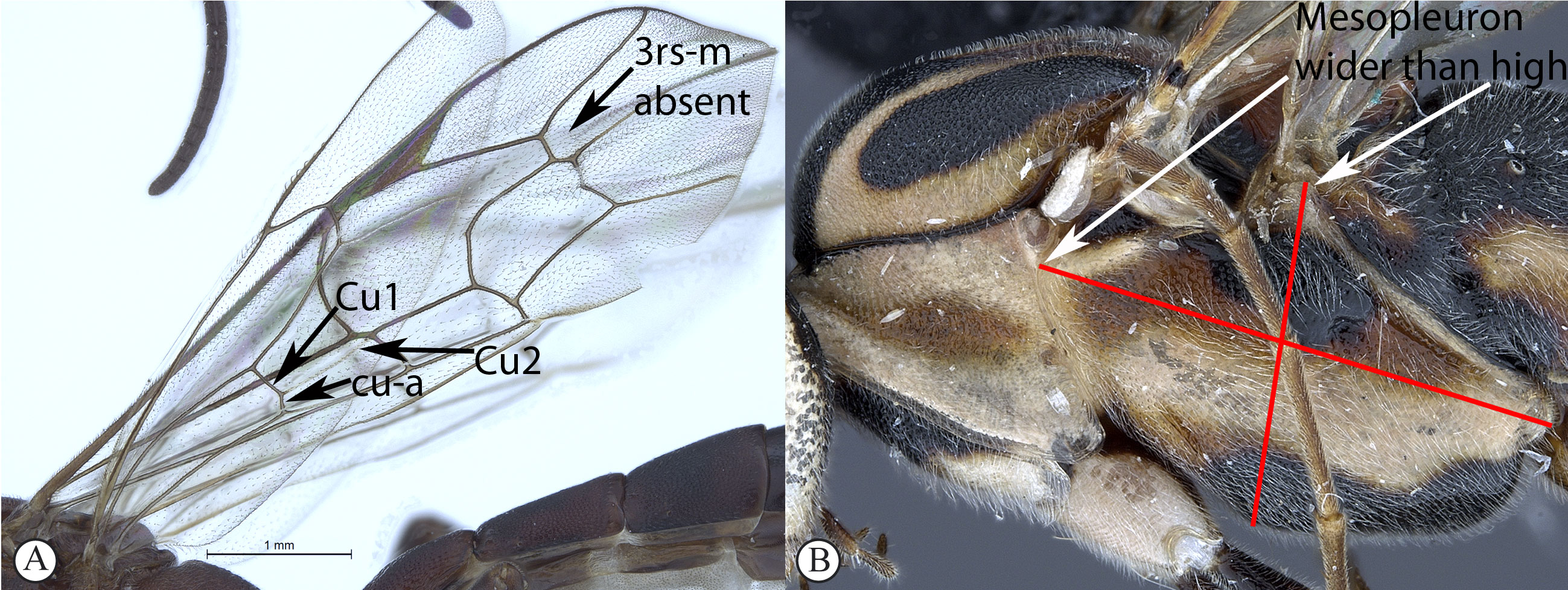
4. Hind wing with Cu1 longer than cu-a such that Cu2 arises below
the middle of these combined veins (nervellus of Townes), rarely Cu2
is absent (A); fore wing with 3rs-m sometimes lacking, shape of
areolet when closed various (A); mesopleuron usually wider than high
(B) ...5
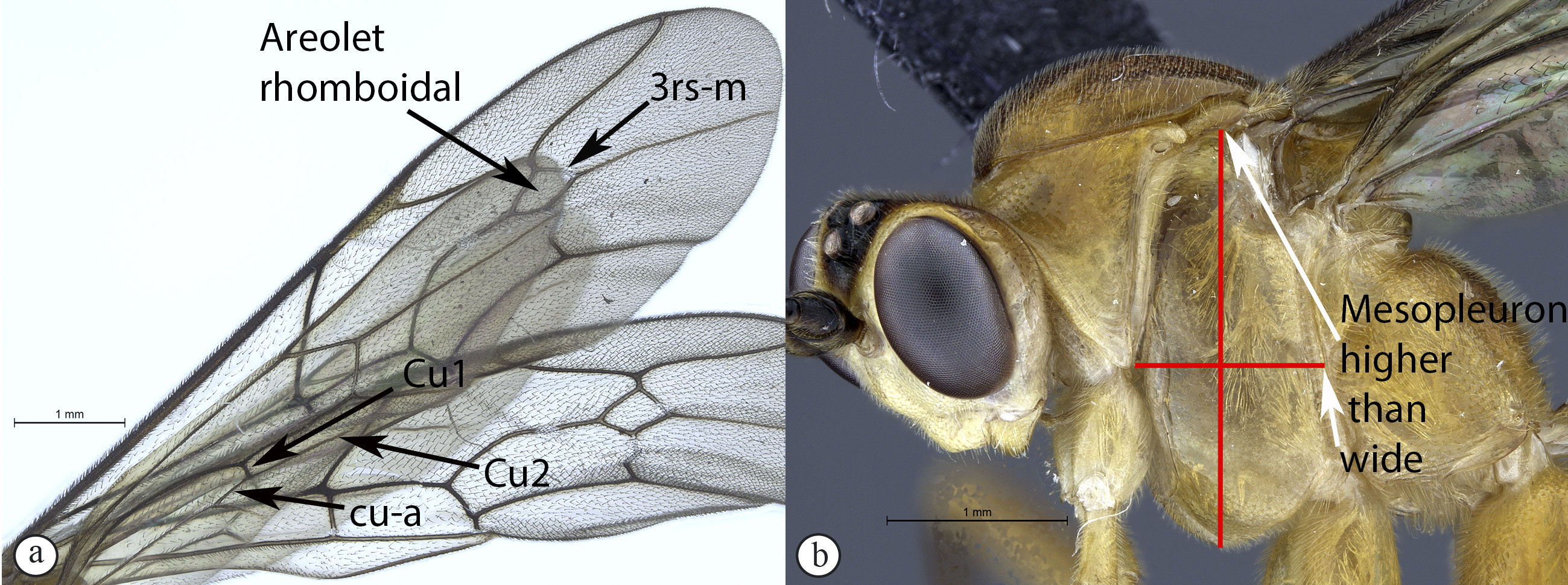
- Hind wing with Cu1 shorter than cu-a such that Cu2 arises above
the middle of these combined veins (nervellus of Townes) (a); fore
wing with 3rs-m always present, areolet rhomboidal (a); mesopleuron
usually higher than wide (b) ...11
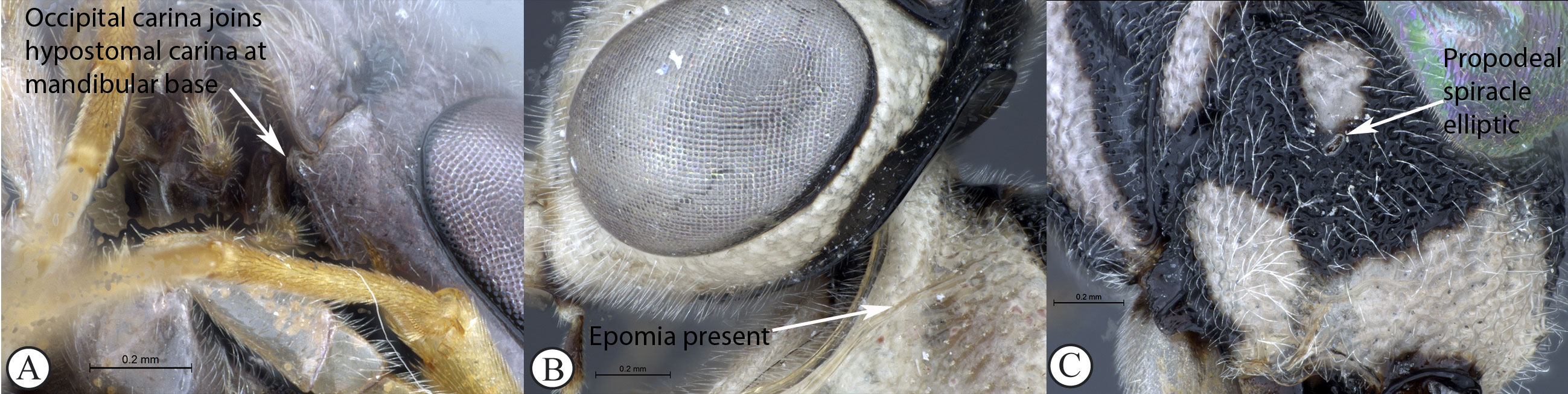
5. Occipital carina joining hypostomal carina at base of mandible
(A); epomia usually present (B); propodeal spiracle elliptic (C) ...Syzeuctus
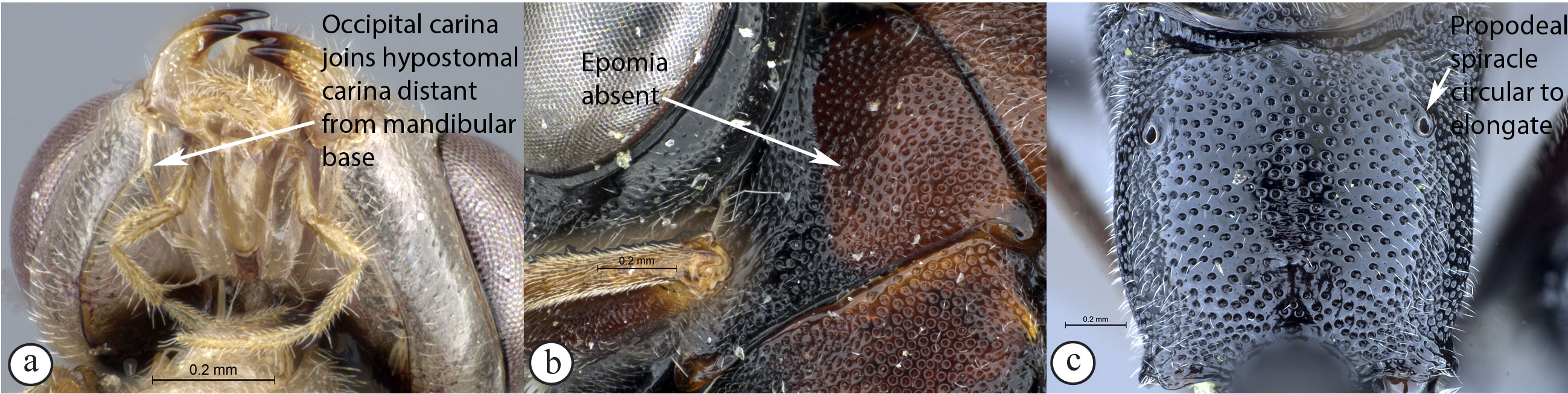

- Occipital carina joining hypostomal carina distant from base of
mandible (a); epomia usually absent (b); propodeal spiracle circular
to elongate (c) ...6
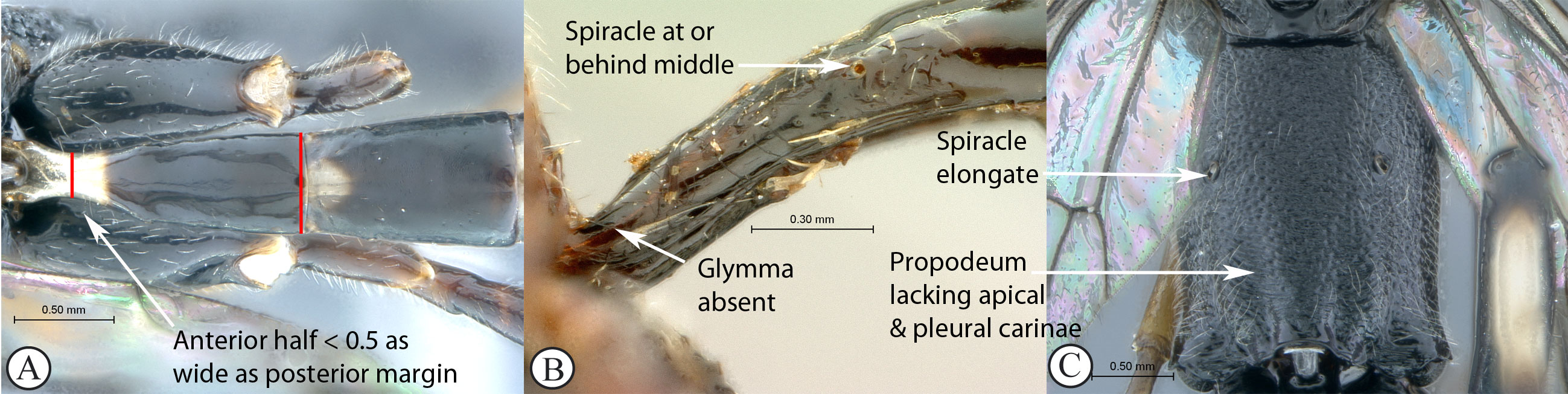
6. Tergite 1 with anterior half slender
(A); glymma absent (B); and its spiracle at or behind
3 middle (A, B); propodeum lacking carinae (C); propodeal spiracle
elongate (C) ...Atropha
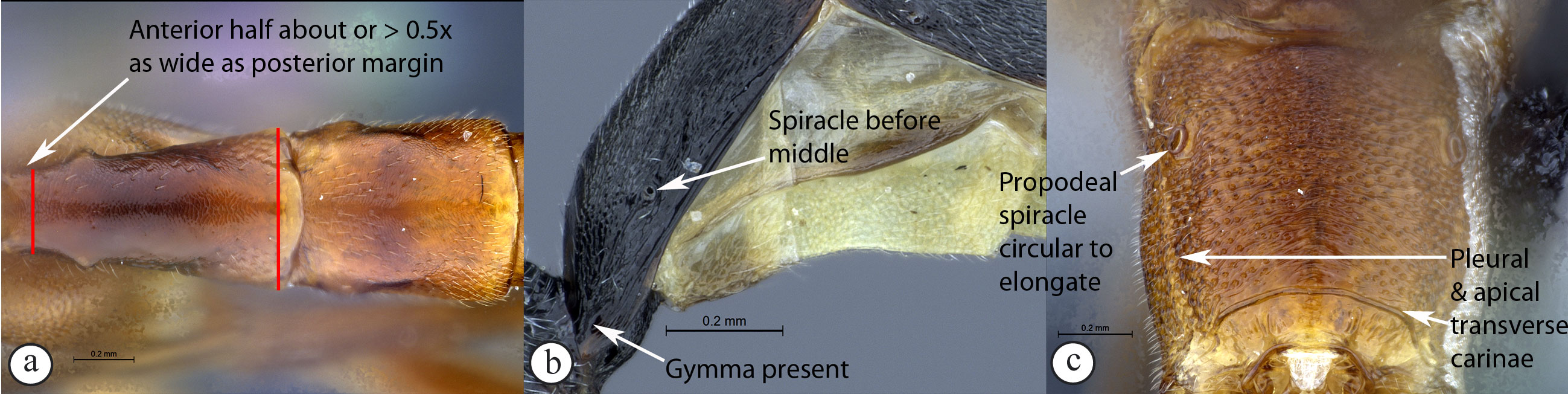
- Tergite 1 with anterior half stout to
moderately slender (a); glymma present (a); with spiracle in front
of middle (a, b); propodeum usually with either an apical transverse
carina or pleural carina, or both (c); propodeal spiracle usually
circular to elongate (c) ...7

7. Apex of submetapleural lobe
tooth-like (A); tarsal claws simple with a single basal tooth above
(B); areolet open (C); occipital carina broadly interrupted above
....Tossinola
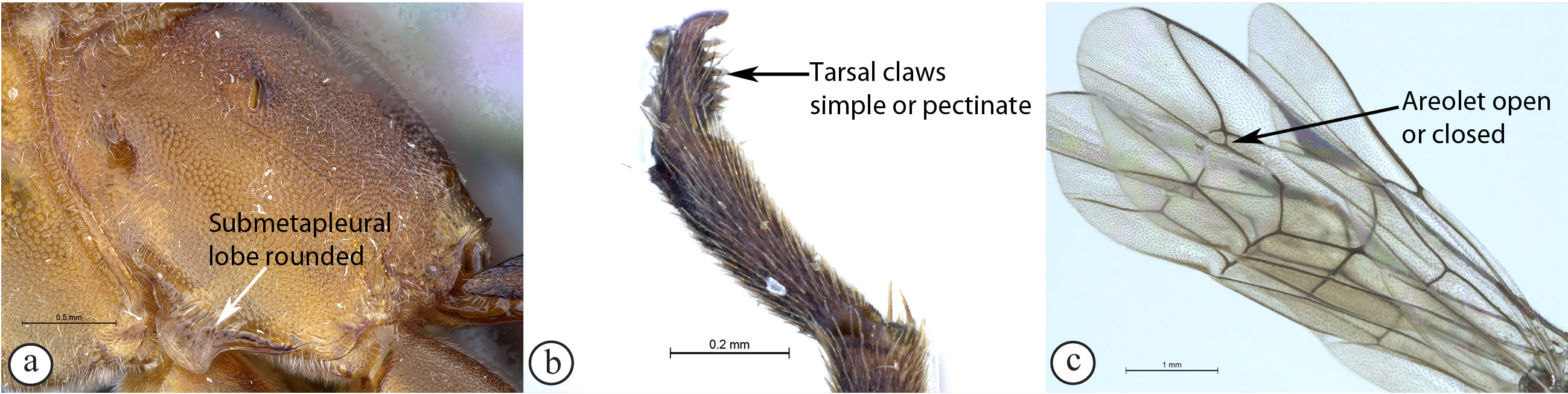
- Apex of submetapleural lobe rounded
(a); tarsal claws simple or pectinate (b); areolet open or closed
(c); occipital carina complete ....8

8. Apical 0.3–0.4 of flagellum tapered
to a slender apex (A); ovipositor sheath 0.6–1.2× as long as hind
tibia (B) ...9
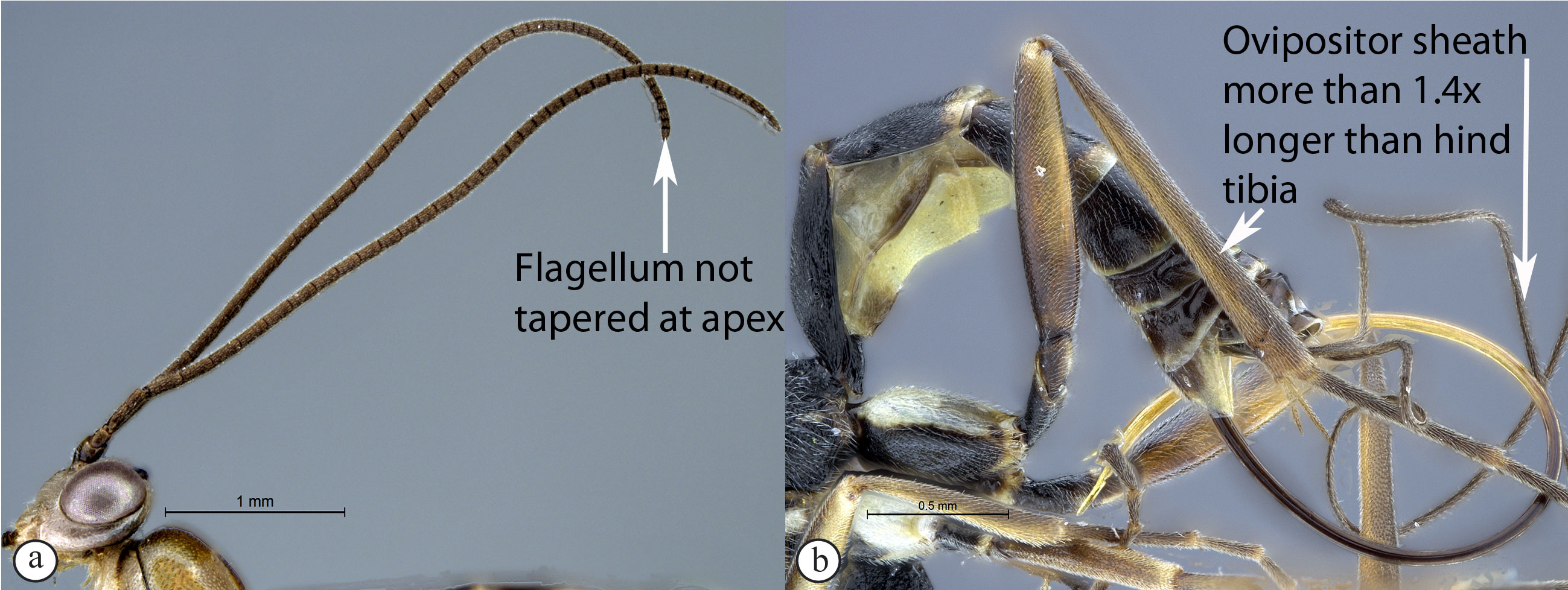

- Flagellum not tapered at the apex (a);
ovipositor sheath usually more than 1.4× as long as hind tibia (b)
...10
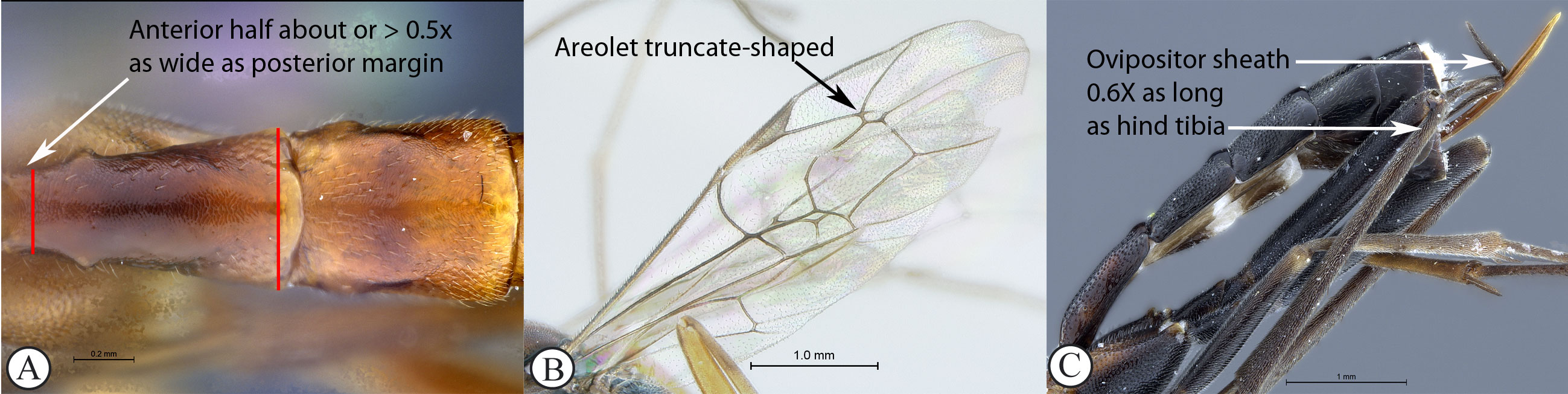
9. First tergite usually evenly and
rather strongly narrowed anteriorly (A); areolet always
truncate-shaped (B); ovipositor 0.6× as long as hind tibia (C) ...Cryptopimpla
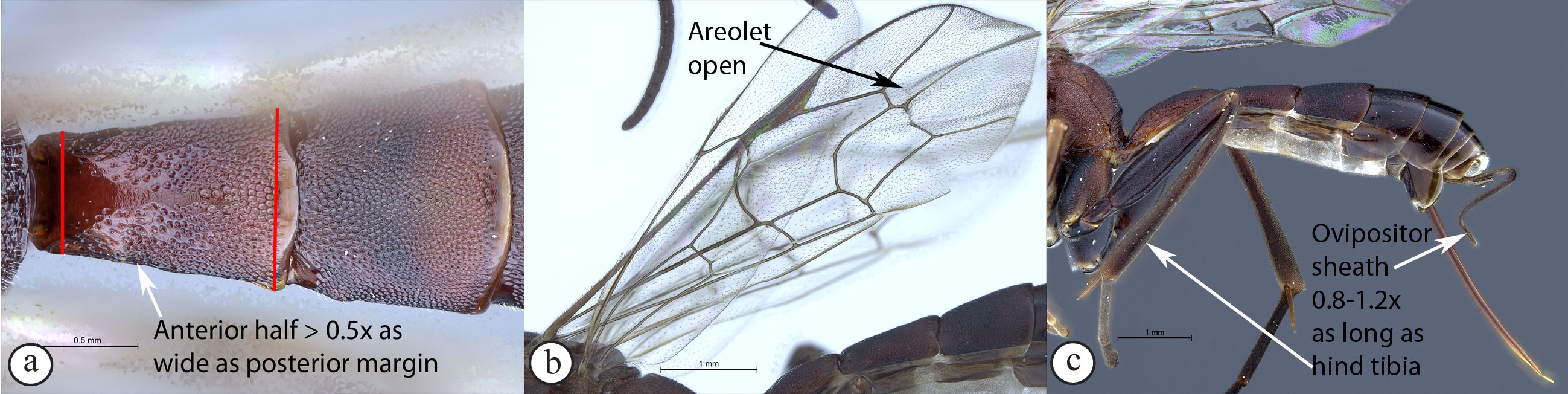
– First tergite stout, only moderately
narrowed anteriorly (a); areolet always open (b); ovipositor
0.8–1.2× as long as hind tibia (c) ....Spilopimpla
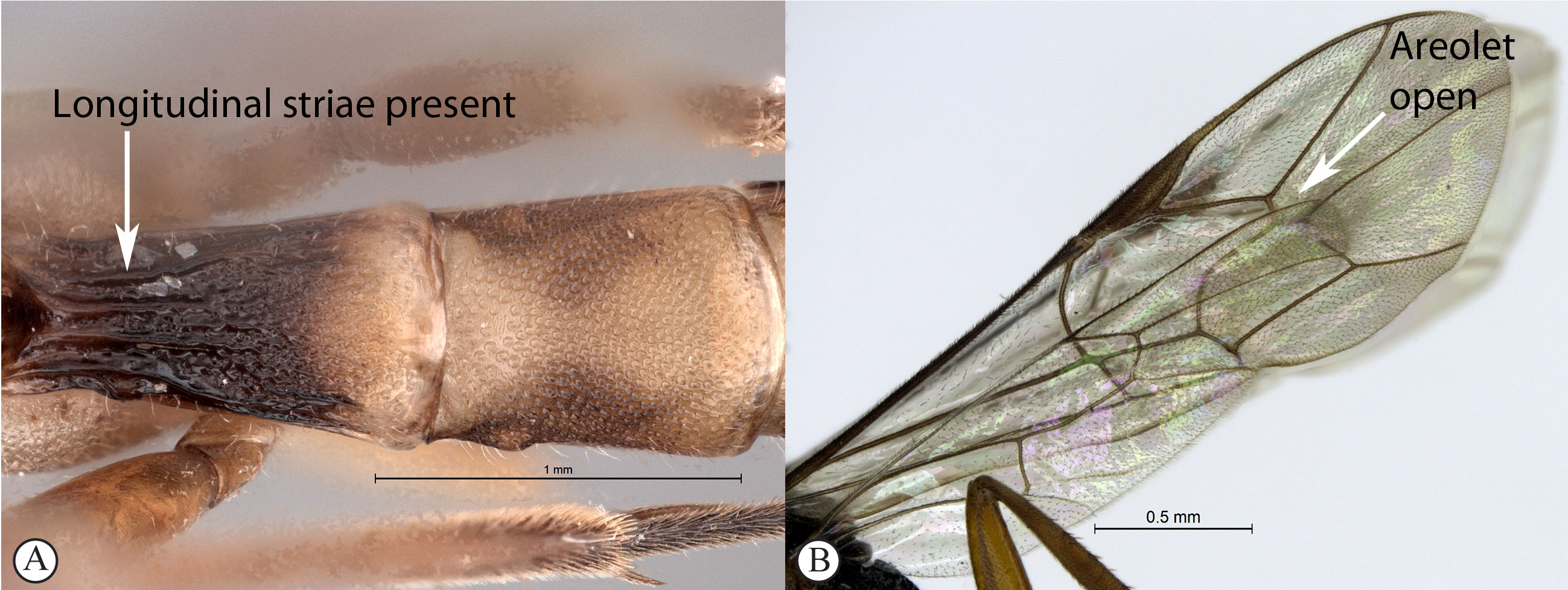

10. First tergite nearly always with
longitudinal striae (A); areolet open (B) ...Himertosoma
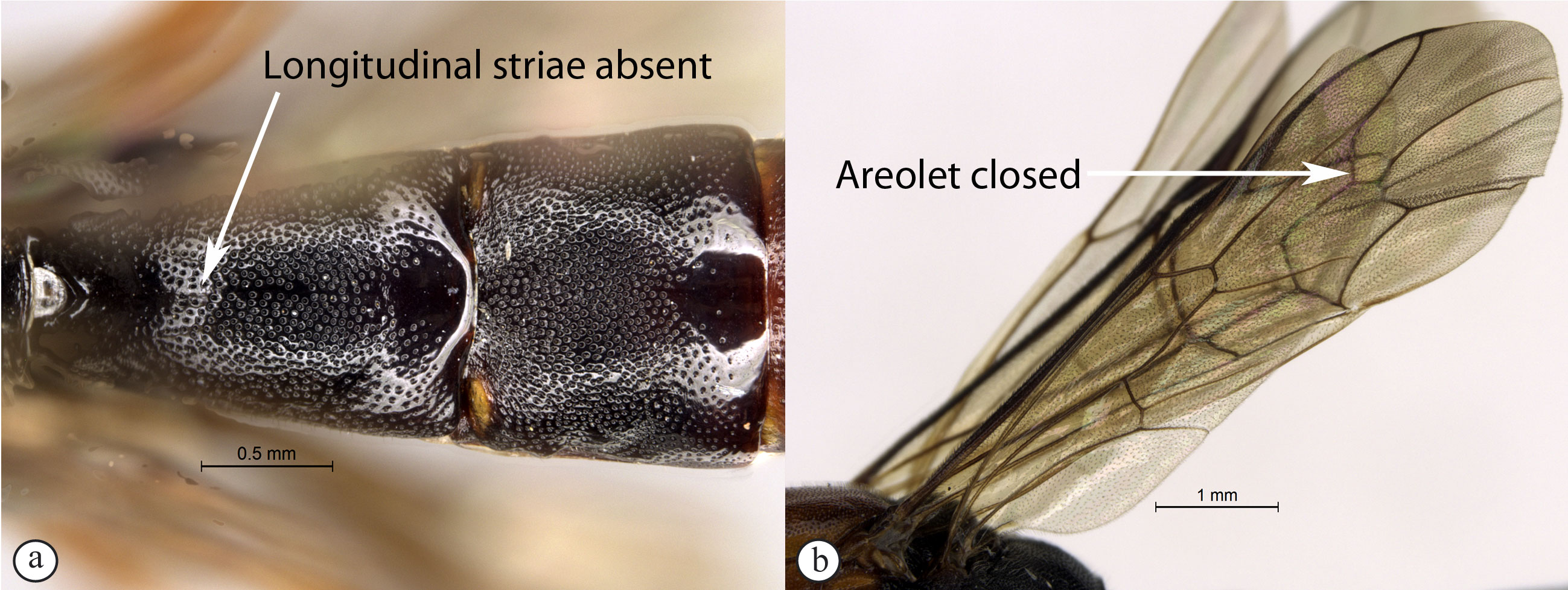

– First tergite rarely covered with
longitudinal striae (a); areolet closed or sometimes lacking (b) ...Lissonota

11. Occipital carina joining hypostomal
carina above base of mandible (A); ovipositor sheath short to long
(0.14–1.8×), as long as hind tibia (B); mandibular teeth usually
subequal in length (C); apical clypeal margin normal (C) ...Exetastes
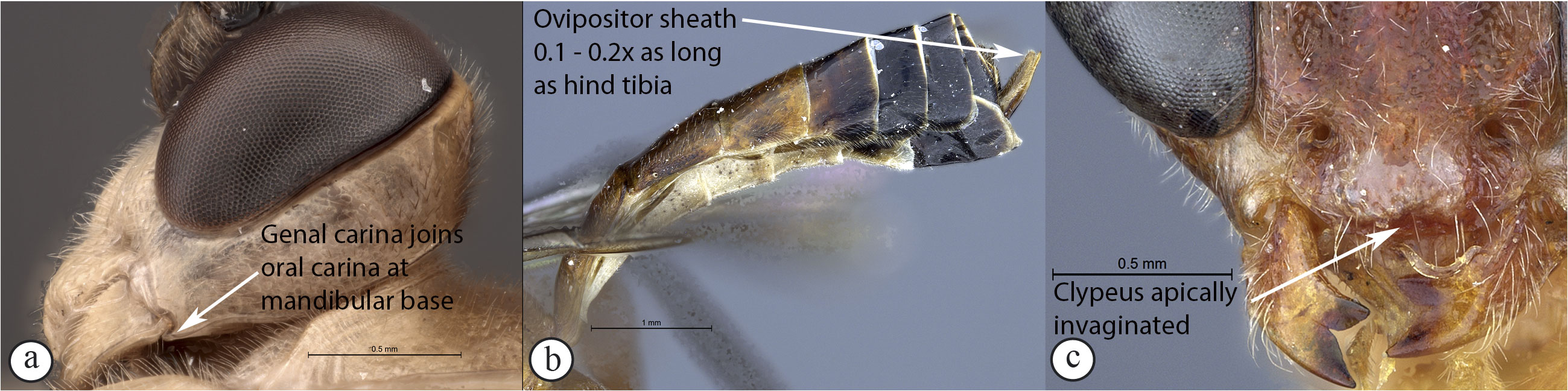
– Occipital carina joining hypostomal carina at base of mandible
(a); ovipositor sheath always short, 0.1 to 0.2× as long as hind
tibia (b); lower tooth of mandible always longer than upper tooth
(c); clypeus apically invaginated (c) ...Tetractenion
|